lab 2
约 803 个字 43 行代码 预计阅读时间 3 分钟
System call tracing (moderate)¶
In this assignment you will add a system call tracing feature that may help you when debugging later labs. You'll create a new trace system call that will control tracing. It should take one argument, an integer "mask", whose bits specify which system calls to trace.
For example, to trace the fork system call, a program calls trace(1 << SYS_fork), where SYS_fork is a syscall number from kernel/syscall.h. You have to modify the xv6 kernel to print out a line when each system call is about to return, if the system call's number is set in the mask.
The line should contain the process id, the name of the system call and the return value; you don't need to print the system call arguments. The trace system call should enable tracing for the process that calls it and any children that it subsequently forks, but should not affect other processes.
Some hints:
-
Add
$U/_traceto UPROGS in Makefile -
Run
make qemuand you will see that the compiler cannot compileuser/trace.c, because the user-space stubs for the system call don't exist yet: add a prototype for the system call to user/user.h, a stub to user/usys.pl, and a syscall number to kernel/syscall.h.
The Makefile invokes the perl script user/usys.pl, which produces user/usys.S, the actual system call stubs, which use the RISC-V ecall instruction to transition to the kernel. Once you fix the compilation issues, run trace 32 grep hello README; it will fail because you haven't implemented the system call in the kernel yet.
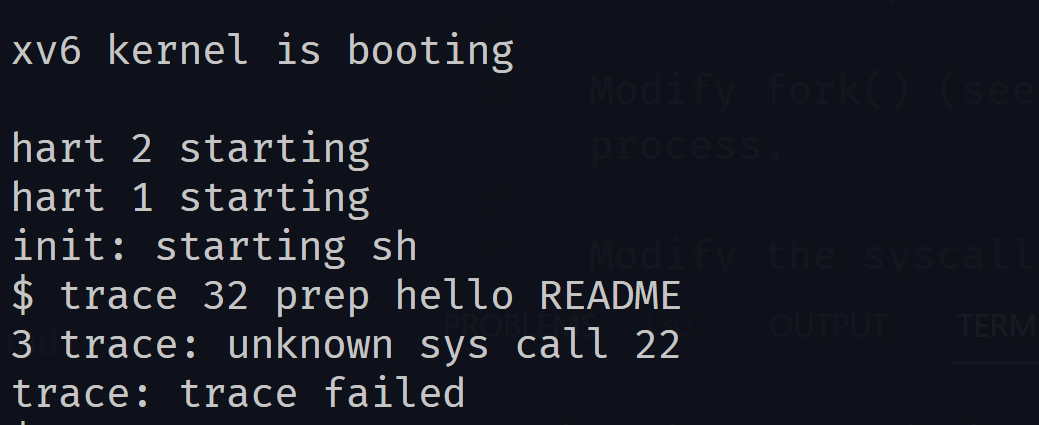
- Add a
sys_trace()function inkernel/sysproc.cthat implements the new system call by remembering its argument in a new variable in the proc structure (seekernel/proc.h).
// kernel/sysproc.c
uint64
sys_trace(void)
{
int mask;
if(argint(0, &mask) < 0)
return -1;
myproc()->mask = mask;
return 0;
}
The functions to retrieve system call arguments from user space are in kernel/syscall.c, and you can see examples of their use in kernel/sysproc.c.
if((p->mask >> num) & 1)
{
// The line should contain the process id, the name of the system call and the return value;
printf("%d: syscall %s -> %d\n",p->pid,syscall_name[num],p->trapframe->a0);
}
-
Modify
fork()(seekernel/proc.c) to copy the trace mask from the parent to the child process. -
Modify the
syscall()function in kernel/syscall.c to print the trace output. You will need to add an array of syscall names to index into.
Exec system call’s implementation in the kernel¶
initcode.S places the arguments for exec in registers a0 and a1, and puts the system call number in a7.
initcode.S把exec的参数放在寄存器a0和a1,把 system call number 放在寄存器a7。
System call numbers match the entries in the syscalls array, a table of function pointers (kernel/syscall.c:108).
system call number 和
kernel/syscall.c:108中的syscalls数组匹配。
The ecall instruction traps into the kernel and causes uservec, usertrap, and then syscall to execute, as we saw above.
当用户程序执行
ecall指令时,它会导致一个切换到内核态的异常,接着执行一系列例程(uservec) , usertrap 和最终的系统调用(syscall)处理。
syscall (kernel/syscall.c:133) retrieves the system call number from the saved a7 in the trapframe and uses it to index into syscalls.
syscall 从在寄存器
a7(trapframe) 中拿到 system call number, 并用它得到 syscalls 中的 索引。
For the first system call, a7 contains SYS_exec (kernel/syscall.h:8), resulting in a call to the system call implementation function sys_exec.
a7中包含的SYS_exec(system call number) 对应着一个 System call 函数 :sys_exec
When sys_exec returns, syscall records its return value in p->trapframe->a0.
返回值存放在
p->trapframe->a0中
This will cause the original user-space call to exec() to return that value, since the C calling convention on RISC-V places return values in a0.
System calls conventionally return negative numbers to indicate errors, and zero or positive numbers for success. If the system call number is invalid, syscall prints an error and returns −1.
系统调用通常返回负数表示错误,返回零数或正数表示成功。如果 system call number 无效,将打印一个错误并返回\(−1\)。
System call arguments¶
The kernel functions argint, argaddr,and argfd retrieve the n'th system call argument from the trap frame as an integer, pointer, or a file descriptor. They all call argraw to retrieve the appropriate saved user register (kernel/syscall.c:35).
有三个参数,(int,address,file descriptor)
The kernel implements functions that safely transfer data to and from user-supplied addresses.fetchstr is an example (kernel/syscall.c:25). File system calls such as exec use fetchstr to retrieve string file-name arguments from user space. fetchstr calls copyinstr to do the hard work.
用
fetchstr来接收字符串。
详细用法都在 kernel/syscall.c 里面写了
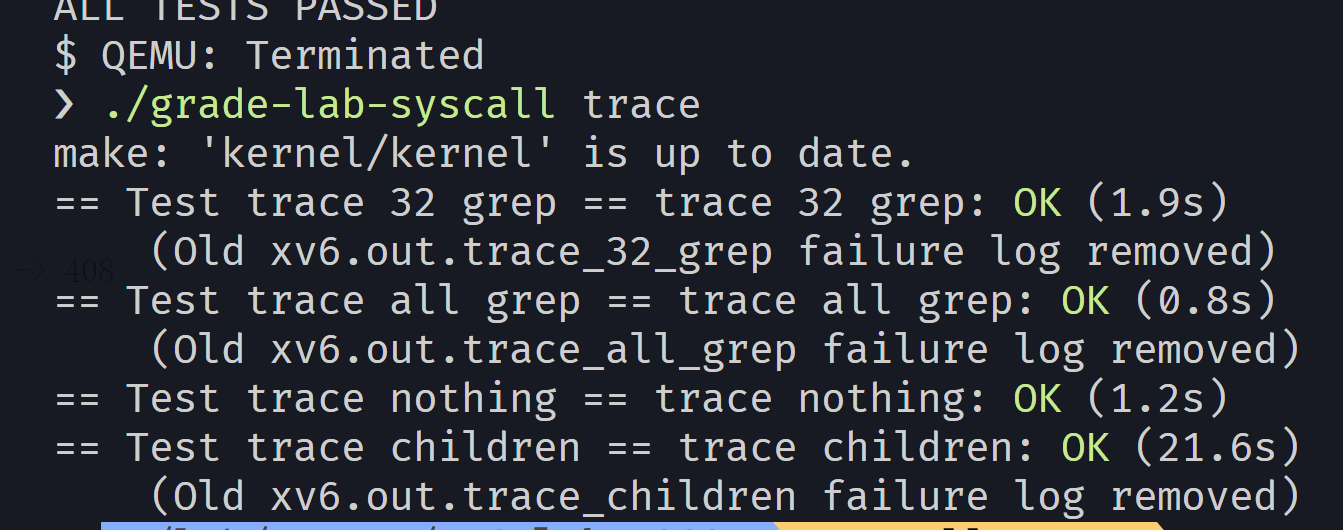
最终结果¶
Sysinfo (moderate)¶
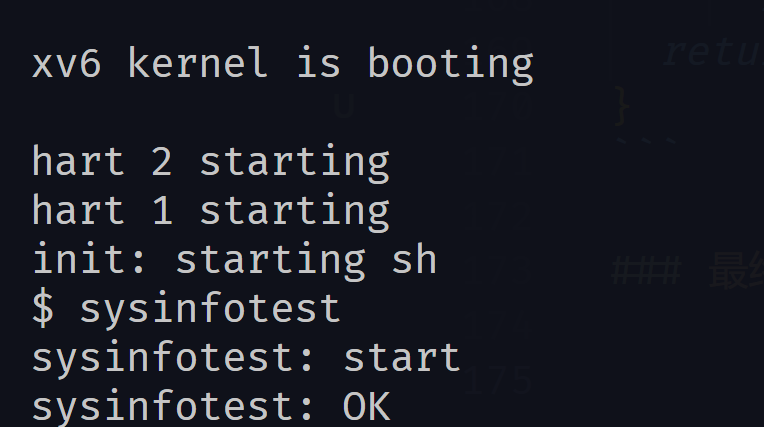
In this assignment you will add a system call, sysinfo, that collects information about the running system. The system call takes one argument: a pointer to a struct sysinfo (see kernel/sysinfo.h). The kernel should fill out the fields of this struct: the freemem field should be set to the number of bytes of free memory, and the nproc field should be set to the number of processes whose state is not UNUSED. We provide a test program sysinfotest; you pass this assignment if it prints "sysinfotest: OK".
Some hints:
- Add
$U/_sysinfotestto UPROGS in Makefile
Run make qemu; user/sysinfotest.c will fail to compile. Add the system call sysinfo, following the same steps as in the previous assignment.To declare the prototype for sysinfo() in user/user.h you need predeclare the existence of struct sysinfo:
Once you fix the compilation issues, run sysinfotest; it will fail because you haven't implemented the system call in the kernel yet.
sysinfo needs to copy a struct sysinfo back to user space; seesys_fstat() (kernel/sysfile.c) and filestat() (kernel/file.c) for examples of how to do that using copyout().
在 user/user.h 写出函数声明,在 user/usys.pl 写出入口,在 kernel/syscall.h 中写出对应的 system call number.
在 kernel/syscall.c 写出 system call number 匹配的函数即 system call function 的入口
sysinfo 结构体:在 kernel/sysinfo.h 中
将该结构体放在 kernel/proc.h 中声明,用于后面的存储信息。
To collect the amount of free memory, add a function to kernel/kalloc.c
To collect the number of processes, add a function to kernel/proc.c
在 kernel/sysproc.c 中写出 具体的函数实现
// sysinfo
extern int collectproc();
extern uint64 kcollect();
uint64
sys_sysinfo(void)
{
uint64 pointer_to_sysinfo ;
if(argaddr(0, &pointer_to_sysinfo) < 0)
return -1;
struct proc *p = myproc();
struct sysinfo info;
info.freemem = kcollect();
info.nproc = collectproc();
if(copyout(p->pagetable, pointer_to_sysinfo, (char *)&info, sizeof(info)) < 0)
return -1;
return 0;
}
最终结果¶
Summary¶
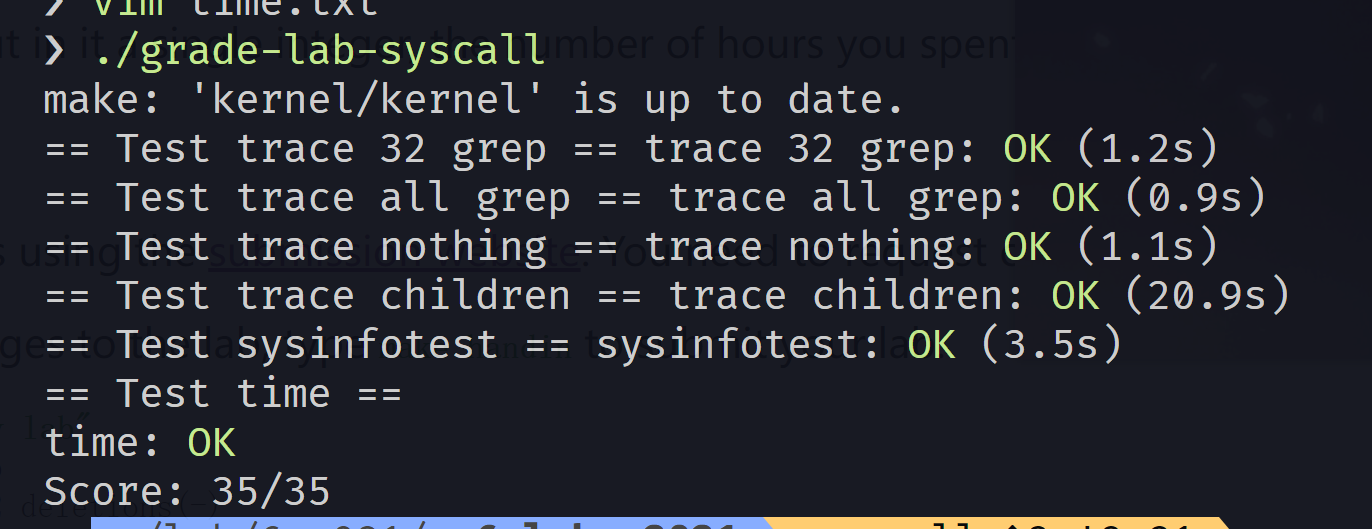
测评命令:./grade-lab-syscall
Created: January 17, 2024